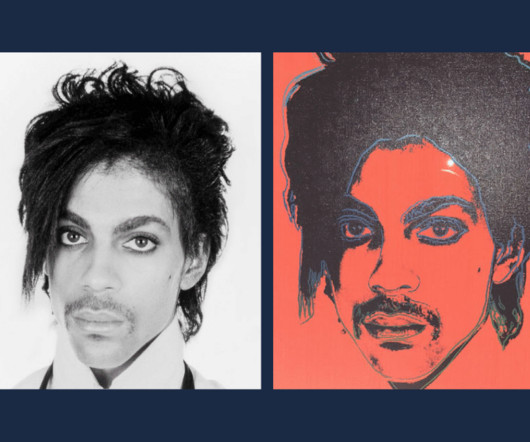
Supreme Court Finds Warhol’s Commercial Licensing of “Orange Prince” to Vanity Fair Is Not Fair Use and Infringes Goldsmith’s Famed Rock Photo
Intellectual Property Law Blog
JUNE 5, 2023
s (AWF), [1] in a long-awaited decision impacting fair use under Section 107(1) of the Copyright Act. Goldsmith and, as a result, did not constitute fair use. [2] Goldsmith and, as a result, did not constitute fair use. [2] Goldsmith was not paid or credited for this use.































Let's personalize your content