False Patent Marking as False Advertising: Overcoming Dastar
Patently-O
APRIL 17, 2024
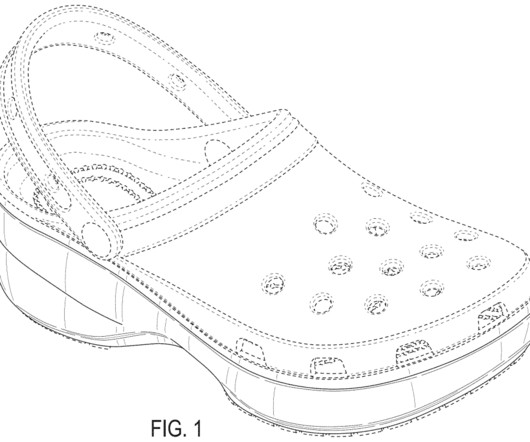
Dawgs’ (“Dawgs”) counterclaim for false advertising under the Lanham Act. This case began back in 2006 when Crocs sued Double Diamond and others for patent infringement of Crocs’s design patents. Crocs largely prevailed in those actions. 1125(a)(1)(B) (Section 43 of the Lanham Act).













































Let's personalize your content