Humanizing Technology: Back to Basics on DABUS and AI as Inventors
IP Watchdog
AUGUST 7, 2021
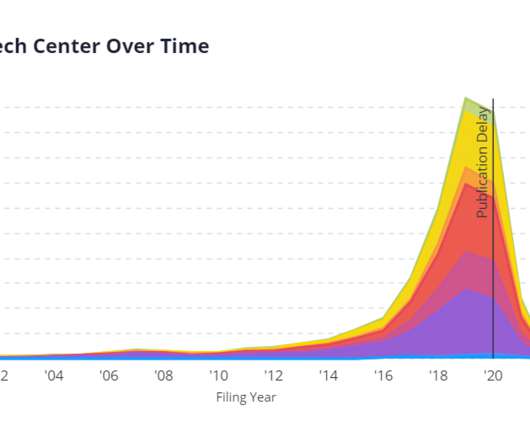
With South Africa’s patent office having recently granted the first patent to an AI inventor, and an Australian court ruling in favor of AI inventorship, it’s time to review how we got here—and where we’re going. If AI-related patent applications and grants are on the uptick, what was the problem with DABUS?























Let's personalize your content