A Comprehensive Look at Data Privacy
LexBlog IP
DECEMBER 28, 2021
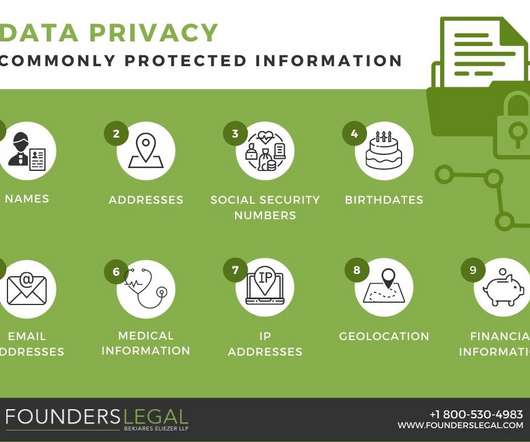
data privacy : what businesses NEED TO know. Keeping pace with the state of data privacy and data privacy regulations is becoming a pressing responsibility for businesses in the digital age. Data privacy legislation is on the rise, with jurisdictions adopting stricter protective measures on a national and global front.











Let's personalize your content