Some Thoughts on Five Pending AI Litigations – Avoiding Squirrels and Other AI Distractions
Velocity of Content
MARCH 16, 2023
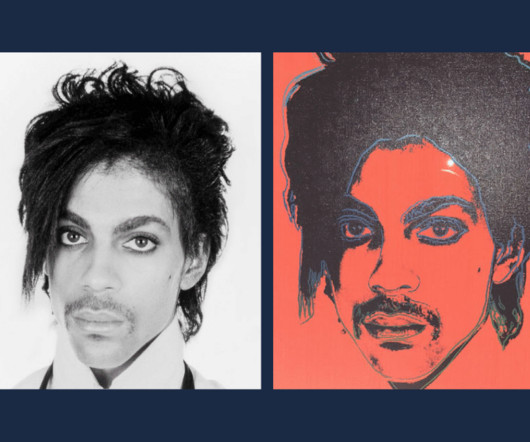
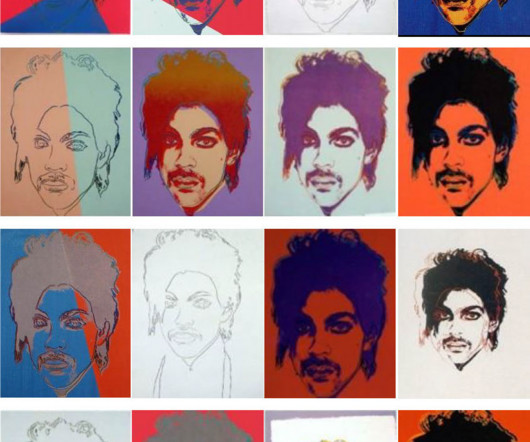
Each of these cases is unique, fact dependent, and likely, if fully litigated on the merits, to shed light on different aspects of copyright law. Below are my thoughts on what is interesting about these cases. Please note that this is in no ways meant to be a comprehensive analysis of the lawsuits. 3:22-cv-06823 – Whither transformative?

































Let's personalize your content